At Hindustan Zinc, proactive risk management is key to sustainable and responsible growth. We ensure this through a robust risk management approach, governance mechanism and framework designed to identify, arrest and mitigate the risks before they can impact on our business. By integrating best-in-class practices and tools, promoting a risk culture and taking a proactive stance on ESG and emerging risks, we effectively navigate challenges and seize opportunities for continued success.
In pursuit of effective risk management, we have engaged Deloitte as our service partner. Their expertise and guidance have been instrumental in navigating the complex landscape of risk within our organisation. This collaboration underscores our commitment to maintaining the highest standards of governance and resilience in the face of evolving challenges.
RISK MANAGEMENT STRATEGY
We have formulated a well-articulated strategy to manage and mitigate the various risks that can potentially impact the organisation. The step-by-step strategic process includes:
- Identification and listing of plausible uncertainties or risks that are likely to prevent us from achieving functional and business objectives, or pose a threat to our business continuity
- Classification of identified risks as internal and/or external, and their categorisation based on their nature or primary causes, velocity or likelihood of potential impact, thereby facilitating effective risk evaluation and response
- Continuous evaluation of risks for timely implementation of mitigation measures
This approach facilitates robust risk management and helps safeguard our operations. At the same time, it enhances our long-term resilience, empowering us to harness opportunities for driving sustained growth and value creation.
Focus on Emerging Risks
We are also cognisant of the importance of identifying and evaluating emerging risks for effective strategic planning, as their materialisation can render critical assumptions during such planning as invalid.
To determine relevant emerging risks, we have initiated global risk sensing. We also encourage employees to submit possible risks for review to the unit risk officers or the Chief Risk Officer (CRO). Additionally, employees are necessitated to stay updated on industry trends through leading publications, participation in sector-specific events, and ongoing engagement with the senior management to identify sectoral trends that can impact the organisation.
RISK MANAGEMENT APPROACH
- Our Board has established an Audit and Risk Management (ARM) Committee to oversee the implementation of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) programme in line with the requirements of the Companies Act, 2013 and SEBI (LODR)
- Our ERM framework is in accordance with leading standards and guidelines. This includes ISO 31000:2018 - Risk Management – Guidelines, Committee of Sponsoring Organisations (COSO): Enterprise Risk Management – Integrating with Strategy and Performance (2017) and various regulations applicable in India
- We follow a comprehensive risk management programme that integrates enterprise risk and risk appraisal for capital expenditure besides mergers and acquisitions, project risks and crisis management. This ensures holistic and consistent risk management practices across our business functions
HINDUSTAN ZINC’S RISK MANAGEMENT SYSTEM IS ISO 31000:2018 CERTIFIED
STRONG RISK GOVERNANCE MECHANISM
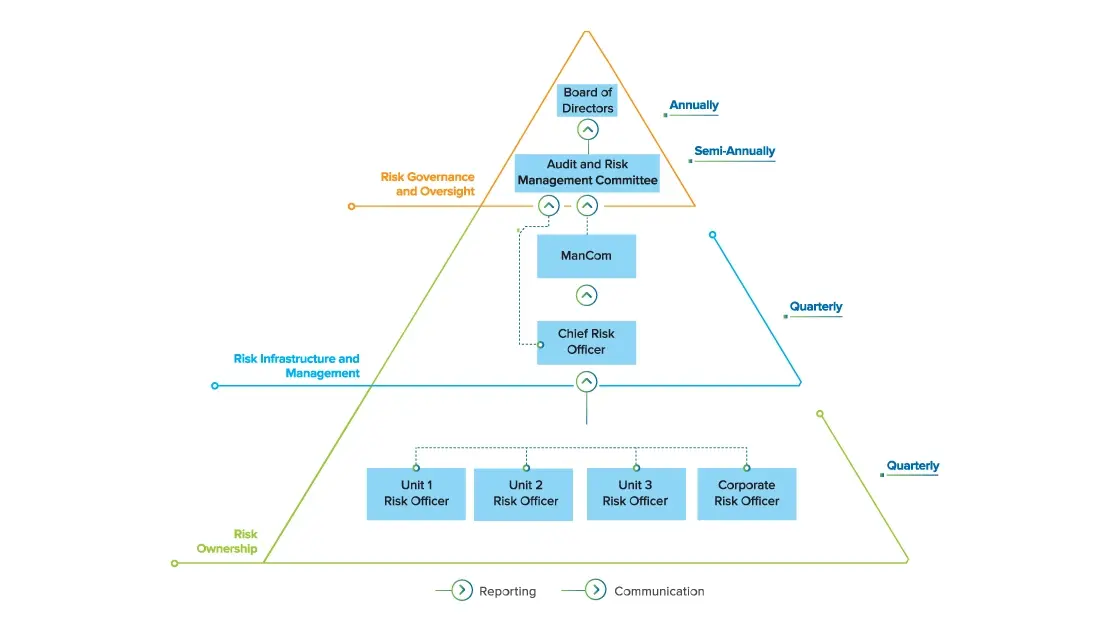
Our 3-tiered defence model and governance structure covers risk oversight, risk infrastructure and management, and risk ownership. It has been established with reference to our organisational structure to ensure integration of the ERM process with management decision-making.
Our risk management framework helps us identify, assess, categorise and address both positive opportunities and negative consequences associated with the business. A robust governance and process architecture enables us to monitor, track and review the risk exposure on a quarterly basis. Roles and responsibilities are clearly defined at each level of the architecture.
Governance structure
- The Board of Directors is responsible for oversight on risk management for the entire organisation; they are also responsible for approving policies that address high-risk areas
- The risk management process at Hindustan Zinc is driven by the CRO at Board level, who reports to the ARM Committee of the Board about existing and emerging risks
- The ARM Committee, comprising three Independent/ Executive Directors with risk management experience, is the highest responsible Committee responsible for the semi-annual review of risk management practices and apprises the Board on risk management in the Company, setting control standards and overseeing compliance with them
- The Management Committee (ManCom) includes risk management matters in its agenda, and ensures timely and adequate mitigation of identified risks
- Operational Level: Each unit has an assigned unit risk officer who is responsible for reporting of unit level risks to the CRO and convenes unit risk councils every quarter to review unit-level risks and response plans
- Independent Audit Unit: Head of internal audit is responsible for monitoring and auditing the risk management performance and providing an independent assurance that the practices are consistent with the Company’s risk strategies and policies. The Head of internal audit also submits a report to the Audit & Risk Management Committee and management assurance system head at the corporate level
Roles and responsibilities of key personnel in risk management
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
- Chairs the Management Committee that undertakes quarterly reviews of Company’s risk exposure and global events which may affect our business
- Reviews are presented before the ARM Committee
Unit/Corporate Risk Officers
- Responsible for identifying and monitoring the risks at the location level
Group-level Management Assurance Function
- Responsible for conducting independent audits and assessment of the risks
- Group management assurance head reports the findings directly to the ARM Committee of the Board
Chief Risk Officer (CRO)
- Monitors and coordinates the risk management framework and facilitates the governance of risk management processes
- Leads the risk team and reports to the CEO
- Supports the management in determining risk appetites, besides identifying trends and emerging risks, and submits report on the principal risks on a semi-annual basis to the Audit and Risk Management Committee
- Monitors enterprise-level principal residual risks on an ongoing basis, reviews the cost, adequacy and effectiveness of the response plans, as well as the accuracy and completeness of reporting
- Guides unit/corporate risk officers, who are responsible for managing risk in their respective business units
- Oversees risk management activities at the operational level
RISK MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK
Our robust risk management framework provides a guided approach for the identification, discussion, measurement and management of vital opportunities and risks faced by us. It outlines clear guidelines to facilitate all our business units and corporate functions to effectively manage risks while pursuing the business strategy.
RISK APPETITE AND TOLERANCE
We have clearly defined our risk appetite and tolerance limits to objectively evaluate our risk-taking ability, facilitating assessment and measurement of the identified risks. The risk appetite, determined by the Board, outlining the risks the Company is willing to take to pursue its business strategy. Risk tolerance puts risk appetite into practice, using quantitative metrics. The impact of any risk is assessed on a 5-point scale. A risk impact of >10% on projected EBITDA (breach of risk tolerance) corresponds to the maximum risk impact score of ‘Very High’ or ‘5’.
Risk Categories
We have categorised the risks based on the World Economic Forum’s assessment categories.

Financial

Operational

Reputational

Regulatory

Project

Cyber Information and Technology

Sectoral

Strategic/ Geopolitical

Sustainability - ESG

Extended Enterprise

Talent

Health and Safety
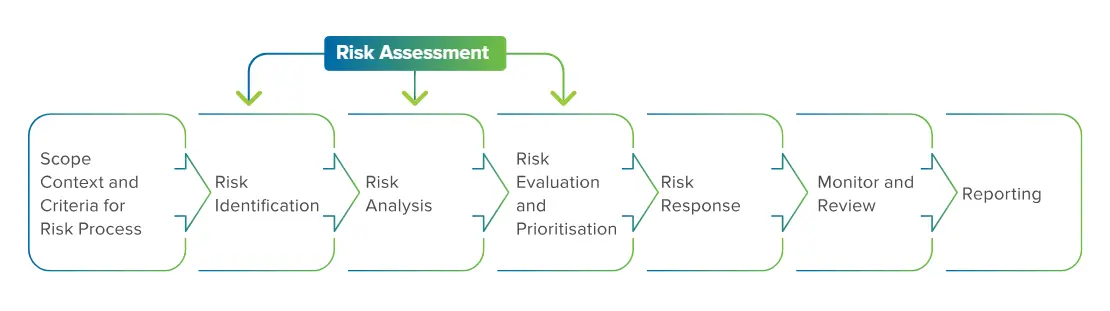
RISK ASSESSMENT
Risk assessment at Hindustan Zinc is a comprehensive exercise, involving:
- Detailing the causes and the associated impact of each risk by the risk owners
- Assessing and mapping of the potential value at risk (in qualitative and quantitative terms) against the impact assessment scales
- Calculation of the impact, likelihood and velocity of each risk, based on potential future impact and historical occurrence of similar incidents, and rating on a 5-point scale
- Calculation of the risk score based on the defined score to identify the risk criticality and prioritise it
A formal monitoring process is used at the unit and
corporate levels to identify and assess the strategic and
financial impact of all risks. This helps in recognising
and classifying the existing and emerging risks and
opportunities into different categories. Risks are then
prioritised based on their frequency of occurrence or
recurrence and the degree of their impact on revenue
and cost, including their potential to disrupt our primary
operations.
RISK IDENTIFICATION
Risk identification involves recognising and listing plausible uncertainties or risks that may impact the successful achievement of our functional, organisational and business objectives, or threaten our business continuity. We also undertake initiative to identify emerging risks although the probability or potential impact of such new or unforeseen risks may not be completely understood. Emerging risks are those that have a limited response plan due to their nature of the risk, but may become a part of the risk register in future.
We employ a multiple-stakeholder approach to ensure effective risk identification. Employees are encouraged to actively participate in the risk management process, facilitating early identification and understanding of emerging risks. We also hold discussions, periodic surveys and risk assessments with key stakeholders, such as customers and suppliers to gain important insights into the risks they face, which may eventually translate into risks for the Company. We further use our understanding of regulatory and legal requirements to anticipate potential risks and the events that typically precede their emergence.
RISK ANALYSIS, EVALUATION AND PRIORITISATION
We consider multiple factors in our risk analysis or assessment. These include understanding the causes, their positive and negative impacts, the likelihood of occurrence and the potential impact and velocity, or the time taken for impact since the occurrence of the risk. A risk score is calculated by rating the impact, likelihood and velocity on a 5-point scale. Such risk analysis helps our management prioritise risks based on the risk score, and deploy necessary response strategies for their effective management.
CONTINUOUS MONITORING AND REVIEW
The ever-evolving and changing nature of risks, their impact, and likelihood necessitates continuous monitoring and review of risks. It is therefore important for us to keep track of the external environment and internal controls as well as our business strategy to better comprehend the risk dynamics. Taking this into consideration, we have defined review forums and cycles for monitoring the risk exposure. We track the risks quarterly, ensuring agility in responding to any change in circumstances. It equips us to promptly implement the necessary controls and actions in time to mitigate them.
We have implemented the following measures to ensure a robust risk monitoring and review system:
- All risk owners are responsible for monitoring the risks allocated to them, which involves continuous gathering of key risk indicator (KRI) metrics associated with each risk
- Risk owners communicate with unit/corporate risk officer on response plans to be implemented (in coordination with the response owner) and their status, and plans for developing new response strategies based on periodic reassessment of risks and effectiveness of mitigations
- Risk owners escalate to unit/corporate risk officer in case of a breach in KRI, especially those falling in the “red” category, indicating a high level of risk
- Quarterly structured risk meetings are convened at the location/unit level and corporate level, wherein principal risks, along with response plans, are reviewed by unit/ corporate risk officers
- Performance of KRIs is tracked either manually or automatically through SAP, which provides a series of “warning lights” to help the risk owner monitor the risk
- Risk owners review principal risks at least quarterly, while moderate and acceptable risks are reviewed biannually and annually, respectively
- In case KRIs for moderate and acceptable risks surpass identified thresholds, risk owners reassess such risks for severity as per the severity matrix, and review these as per the frequency of the revised classification

MONITOR & REVIEW
ONGOING
Unit/Corporate Risk Officer
- Risk Identification and Assessment
- Risk response planning
QUARTERLY
Chief Risk Officer
- Review of principal risks for every business unit or subsidiary
- Review of severe & critical risks, emerging risks and inputs from global risk sensing report
Unit/Corporate Risk Officer
- Review of severe & critical risks
- Review of principal risks for every business unit or subsidiary
BIANNUALLY
Chief Risk Officer
- Review of principal risks for every business unit or subsidiary
- Review of moderate risks
ANNUALLY
Audit & Risk Management Committee
- Reporting of principal and emerging risks to Board
We have further implemented the SAP governance, risk and compliance (GRC) risk management module, which encompasses various features to enhance the risk management process:
- Workflow-based process for risk submission, assessment and mitigation planning to ensure employees can submit risks for approval at senior levels
- Automated assessment of risks based on inputs relating to ‘value at risk’ and ‘probability’ of occurrence
- Stress testing and sensitivity analysis conducted using scenario modelling and simulations through a ‘what-if’ analysis and techniques like Monte Carlo simulation – to predict a range of possibilities and outcomes for an uncertain event
- Automated KRI monitoring
- Automated notifications for triggering of assessments, breach of KRI, and pending activities, along with relevant escalations
We use SAP risk management for all risk management processes, ensuring greater control over risks monitoring, mitigation strategies implementation, occurrence tracking, and reporting to senior management and the Board.
During FY 2023-24, an external surveillance audit was conducted for the continuation of our ISO 31000:2018 certification. An internal audit of the risk management process was also conducted during the year.
EMBEDDED IN RISK CULTURE
All business functions at Hindustan Zinc follow a culture of proactive risk management. We take regular initiatives to create awareness, discuss risk mitigation, and encourage risk-focussed discussions across our hierarchy to foster such a culture.
The various measures to promote a risk culture and enhance risk awareness across the organisation are as follows:
Incentivising Risk Management
- Risk management and mitigation linked to the KPIs of senior management, including the CEO, and other employees encouraged them to participate in risk management activities
- Annual financial incentives linked with the outcome of KPIs and active participation in risk management activities
Continuous Improvements in Risk Management Practice
- Progressive enhancement in risk management processes and response action plans
- Quarterly risk review meetings by unit risk officers to review existing risks and deliberate on new risks identified with unit-level stakeholders
- Teams across hierarchies to report any type/category of risk through accessible online reporting platforms (including escalation windows)
Risk Appraisal for Capital Projects
- 3-step process for capital expenditure risk assessment prior to the approval of both payback and non-payback projects, including for new product development projects
- Mandatory risk assessment for capex projects by the project team to highlight critical project risks
- Mandatory risk assessment by the central risk team for all growth projects, unbudgeted capex for non-payback projects, and sustenance payback projects above a certain threshold
Promoting Risk Education and Training
- Regular refresher training and awareness sessions for senior management on identification, resilience planning and mitigation of various risks as deemed necessary by the Board
- Individual training sessions for Executive and non-Executive Board members, including ARM Committee members, to familiarise them with the risk management process and global risk trends
- Organisation-wide trainings and workshops on risk management topics to strengthen risk knowledge and implement a risk-intelligent culture
- E-mail circulation on specific risks to generate awareness among the workforce
Incorporating Risk Criteria in Product and Service Development
- Risk considerations factored into the entire product lifecycle - from sourcing to product development, management, technology and market risks
- Business partner risks with the potential to affect the product development process are managed through risk management frameworks, standard operating procedures (SOPs) and robust BP management policy
- Rigorous review of product development risks including changes in customer expectations or regulatory requirements, followed by necessary process adaption to proactively mitigate them; the R&D department addresses innovation and product application risks through pre-commercialisation piloting and testing
Integrating Review Process for HR
- Individual performance of employees is linked to KPIs related to sustainability, safety, risk and compliance, including proactive risk reporting and timely completion of risk management/ action plans as defined on the digital portal, etc.
- Use of innovative risk management solutions to identify and implement risk management plan
Facilitating Risk Identification and Disclosure
- Risk reporting considered as a responsibility of all employees
- Unit/corporate risk officers, in charge of assessing risk at each unit/location, designated as a single point of contact for employees to report risks
- Risks uploaded onto a digital platform for proactive monitoring and reporting of risk indicators/risks
Mitigating Business Partner Related Risk
- Robust process in place to identify and mitigate business partner (BP) related risks and ensure production continuity
- Regular review of KPIs and BP engagements to discuss emerging or potential risks
To ensure the continual strengthening of our risk mitigation and management framework, we clearly define risk management targets and indicators as part of our risk scorecard. Additionally, performance evaluation is undertaken at the management and higher levels on a regular basis.
Criteria empowering our Business Partner Management Policy
Selection of business partners with turnover exceeding a specified limit, subject to exceptional approval from CCO/CFO/CEO
Strict adherence to no dealings with trader entities
Regular assessment of KPIs through quarterly scorecard ratings to ensure ongoing alignment and performance evaluation
FOCUS ON ESG RISK MANAGEMENT
Hindustan Zinc priorities open and transparent engagement with stakeholders for enhancing trust and driving sustained growth. This is in line with our growing focus on all Environment, Social and Governance (ESG) facets, including the related risks.
We strive to maintain continuous interaction with our stakeholders, to understand their perspectives and swiftly respond to the evolving market scenarios. We conduct materiality assessment to identifying topics of significance for our internal and external stakeholders, guiding our strategies for managing the risks and harnessing the opportunities. This robust process strengthens our sustainability approach by facilitating the identification and understanding of the most material ESG priorities.
Climate change & decarbonisation, air emissions & quality, and water management have been identified as the top three material topics for Hindustan Zinc. Biodiversity and climate change are acknowledged as key parameters in enterprise risk management due to their array of associated risks, including regulatory, operational, reputational, financial, market access, and physical risks. ESG considerations, including biodiversity and climate, are seamlessly integrated into our overall business strategy. From the inception of any project or initiative, we assess its potential ESG impacts, and incorporate risk mitigation measures accordingly. Our ESG risk management process takes a holistic view of risks and opportunities, recognising the interconnected nature of ESG factors to address them comprehensively rather than in silos.
Risk Rating
Very Low
Low
Medium
High
Very High
Risk Appetite Level
Low
Medium
High
Very High