The materiality assessment serves as a vital tool, not only in identifying significant sustainability matters pertinent to our business but also in deepening our understanding of stakeholders’ views that reflect the impact of the Company’s activities and expectations from the Company on sustainability matters. Additionally, it enables us to proactively address the rising demand for integrated reporting, ensuring alignment of sustainability matters with industry-leading practices.
Our ESG committee at Board approves and signs off on the material issues. The same is then circulated to all the relevant functions and teams for taking relevant actions to address the impact. We also follow an annual assurance process, as part of which a third-party validates our approach on materiality, and ascertains its relevance in the context of our business and sector.
Identifying list of material topics
An initial lengthy list (of 85 topics) was identified by utilising leading standards based on the various emerging risks & opportunities.
The list was then cut down with further assessment to create an exhaustive list (of 24 material ESG topics) for Hindustan Zinc, based on four leading standards covering the concept of double materiality, and inputs of materiality faced by peer companies of Hindustan Zinc.
Gathering stakeholder inputs
For data collection, stakeholder-specific data tools like interview and survey questionnaires were developed.
Inputs were collected from seven groups of stakeholders (483 nos.) through interviews, focus group discussions and surveys.
This included both qualitative and quantitative inputs to better understand stakeholder perceptions about Hindustan Zinc’s impact on environment and society.
Risk and opportunity analysis
We analysed the potential impact of the identified issues on Hindustan Zinc’s ability to execute its business strategy and those with financial implications.
These topics were then assessed against the risk threshold as defined in the enterprise risk management matrix.
Finalisation of materiality matrix
Determination of the high impact material issues was based on the risk & impact assessment and stakeholder responses that are analysed using a scoring methodology.
On the basis of severity, remediability and likelihood of occurrence, these issues were classified as high-high and medium-high impact areas.
The materiality matrix was developed following a thorough analysis of all stakeholder’s data.
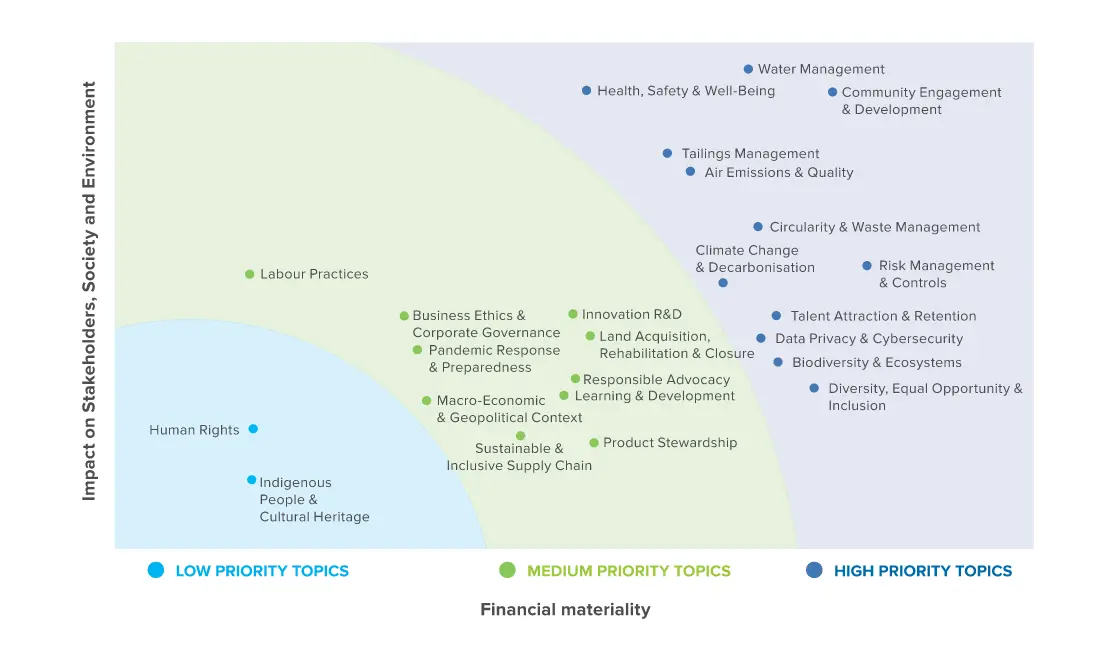
We concluded that each impact level requires a differentiated management approach, and accordingly formulated a unique strategy across each category, based on the level of risk, opportunity and/or impact.
Our category-wise strategic actions are based on their importance to our business. They take into account our materiality assessment, as well as the priority assigned to each material topic. We have also initiated a management approach to guide our actions in each priority area. This involves identification of specific programmes to address each material issue, based on its priority ranking. These programmes are being rolled out gradually, in phases, across the organisation.
| High PriorityMaterial Topic | KPIs | Strategylinkage | SDGlinkage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Climate Change & Decarbonisation |
Achieving net zero emissions by 2050 or sooner |
S4
S5
|
|
0.5 mn tCO2e GHG emission savings in our operations in 2025 from base year of 2017 |
|||
| Air Emissions &Quality | Reduction in non GHG emission (SOx and NOx emission) by 17% by 2025 from base year of 2020 |
S5 |
|
| WaterManagement |
Become 5x water-positive Company and achieve 25% reduction in fresh water usage by 2025 from base year of 2020 |
S5
|
|
| Circularity &Waste Management | 3x Increase in gainful utilisation of smelting process waste by 2025 from base year of 2020 |
S2
S5
|
|
| Tailings Management |
Complete transition from wet tailing to dry tailing disposal by 2025 |
S1
S2
S5
|
|
| Biodiversity & Ecosystems |
Protect and enhance biodiversity throughout the life cycle |
S5
|
|
| Community Engagement &Development |
Positively impacting 1 million lives through social, economic and environmental initiatives by 2025 |
S5
|
|
| Health, Safety & Well-Being |
Zero work-related fatalities and 50% reduction in Total Recordable Injury Frequency Rate (TRIFR) by 2025 from base year of 2020 |
S5
|
|
| Talent Attraction & Retention |
Inclusive and diverse workplace with 30% diversity by 2025 |
S5
|
|
| Diversity, Equal Opportunity& Inclusion |
Inclusive and diverse workplace with 30% diversity by 2025 |
S5
|
|
| Data Privacy & Cybersecurity |
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
|
|
|
Hindustan Zinc remains steadfast in its commitment to consistently assess the impact of diverse sustainability matters on its business. We accordingly focus on adapting our strategy to the assessment and in line with the evolving external dynamics. Critical areas like safety, climate change, biodiversity management, human capital management, community management, etc., which are listed among the risks faced by the Company, have been identified as material issues. This makes it extremely important for us to address these through an integrated strategic approach.