| Material theme | Our strategic priority | SDGs impacted | Sustainability Goals 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Climate Change & Decarbonisation |
S5
Progressing towards a sustainable future |
0.5 mn tCO2e greenhouse gas (GHG) emission savings in our operations from base year 2017 | |
| Water Management |
S5
Progressing towards a sustainable future |
Become 5x water positive company and achieve 25% reduction in freshwater consumption | |
| Tailings Management |
S5
Progressing towards a sustainable future |
Transition from wet tailings disposal to dry tailings disposal by 2025* | |
| Air Emissions & Quality |
S5
Progressing towards a sustainable future |
Reduction in non GHG emission (SOx and NOx emission) by 17% by 2025* | |
| Biodiversity & Ecosystems |
S5
Progressing towards a sustainable future |
Protect and enhance biodiversity throughout the lifecycle 1 million plantation drive by 2025 |
|
| Circularity & Waste Management |
S5
Progressing towards a sustainable future |
3x increase in gainful utilisation of smelting process waste |
The fast-paced energy transition taking place globally, coupled with the aggressive shift towards climate change mitigation, has led to enhanced investments in this area by both developed and developing nations. Manufacturing and sale of solar photovoltaic (PV) panels and energy storage solutions has witnessed significant growth in recent years amid the global transition towards net-zero carbon emissions. This is catalysing increased demand for our products – zinc, lead and silver.
We are proactively augmenting the capacities and capabilities at Hindustan Zinc, in line with the evolving market trends, to meet the growing demand for our highquality products. As a part of the Company’s net-zero journey, we are also focussed on scaling its innovation capabilities and sustainability thrust.
Our net-zero journey is powered by our climate actions, which in turn are driven by our stringent emission targets. The strength of our initiatives has been validated by the recent approval accorded by Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) for our near-term and long-term net-zero targets. Hindustan Zinc is among the few Indian companies in the mining sector with validated and approved SBTi targets in alignment with 1.5°C – an ambitious campaign led by SBTi in partnership with the UN Global Compact and the ‘We Mean Business’ coalition.
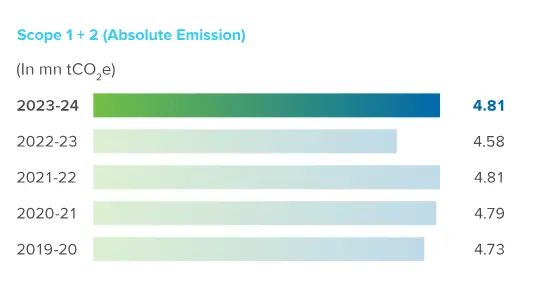
In the short term, our targets are aimed at helping the Company reduce its scope 1 and 2 emissions by 50% and scope 3 emissions by 25% by 2030 from the baseline of FY 2019-20. In the long-term, we will steer Hindustan Zinc’s journey towards net-zero emission by 2050 or sooner.
Propelled by these stringent targets, we have been continuously enhancing our renewable energy transition over the past few years. Our total green power capacity includes 273.5 MW of wind power (non-captive), 40.70 MW of solar power (captive) and 48.46 MW of waste heat recovery power. Going forward, we shall strive to further expand renewable power under our greenhouse gas reduction goals.
Further supporting our energy transition journey is the sourcing of 100% green power for the operations at Pantnagar Metal Plant, which we achieved last year. This one-of-a-kind initiative is helping us reduce emissions by more than 30,000 tCO2e per annum. We have successfully reduced another 76,035 tCO2e of emission by minimising our coal consumption through use of biomass as an alternative fuel.
We acknowledge the importance of aligning our upstream and downstream suppliers to our goals. We conducted several training sessions during FY 2023-24 to create awareness amongst them on topics such as climate change, biodiversity, no net loss and human rights.
In 2022, Serentica Renewables India Private Limited (’Serentica’) was founded with a singular vision to decarbonise India’s industrial sector, which is one of the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. It aims to become a leading sustainable energy platform to accelerate clean energy transition for ‘hard-to-abate’ industries by providing round-the-clock renewable energy, through a blend of solar, wind and energy storage solutions.
True to its commitment and with c.1,800 MW of power delivery agreements (PDAs) signed till date, Serentica has emerged as the decarbonisation partner of choice for India’s largest consumers of electricity in the aluminium, steel, chemical, oil & gas, and mining sectors. To meet the round-the-clock renewable energy requirement, the company is building c.4,000 MW renewable energy projects across the states of Karnataka, Maharashtra and Rajasthan.
Serentica is on course to develop 5 GW of renewable energy capacities across the country to deliver round-the-clock to the green energy needs of its customers. By 2028, it plans to supply over 50 bn units of clean energy annually, and displace 47 Mt of CO2 emissions.
Partnering with Serentica (SRI4PL & SRI5PL), Hindustan Zinc, in FY 2022-23, entered into renewable energy PDA for Dariba (200 MW) and Chanderiya (250 MW) plant locations. The 180 MW Bikaner solar power project is the centrepiece of this strategic partnership, and has been completed a year ahead of the schedule. Phased completion and commissioning are planned till June 2025 with the first power flow started from May 2024.
As a cornerstone of Hindustan Zinc’s decarbonisation strategy, this arrangement provides the Company with multiple benefits, including:
Electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as a major alternative to reducing the dependence on petroleum products. Companies worldwide have embarked on EV and alternate fuel journeys to reduce their CO2 emissions. In line with this trend, which is picking up momentum in India too, we further augmented our fleet of battery-operated EVs for use in our underground (UG) operations during FY 2023-24 to steer us towards our net-zero goal. Having become the first Indian company to deploy underground battery electric vehicle (UG BEV) in SKM in the previous fiscal, we scaled up our investments in this area in FY 2023-24 by deploying two more UG BEVs to reduce emissions and move towards sustainable mining.
We have also deployed passenger EV vehicles, EV forklifts and EV light motor vehicles in our operations, as a part of our commitment to decarbonisation and reduction of the environmental impact on our business. In addition, we have made inter-unit transport more sustainable with the deployment of 10 EV trucks of 55 metric tonnes capacity each. These initiatives will help reduce scope 3 emissions and enable us to progress towards our SBTi targets.

In addition to zero emission and reduction in the mine carbon footprint, EVs provide a host of other key advantages over the diesel-operated vehicles. These include the lower cost and time involved in their maintenance, quicker commissioning, lesser ventilation requirement, besides elimination of diesel and lubricant storage, transportation and handling. EV deployment in mines also helps improve the ambient air condition underground, leading to better health for the underground workers.
Cumulative energy savings
Solar power produced
Waste heat energy produced
Wind power produced
Board-level ESG Committee
Executive Sustainability Committee and Energy and Carbon Community
SBU ESG Committee
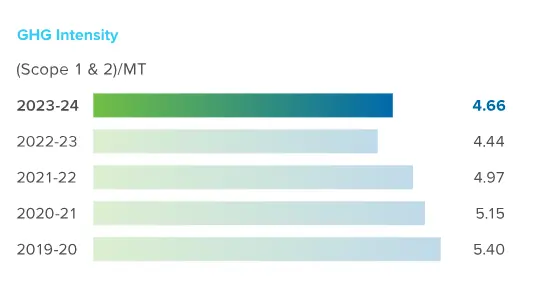
Our sustainability ethos extends to the precious water resource, and we continue to make investments in optimising the water usage at Hindustan Zinc. Our efforts are aimed at reducing our freshwater dependency through innovative water recycling initiatives. They are driven by our goals to:
To steer the realisation of these goals, we have embraced the vision of ‘Zero Harm, Zero Waste, Zero Discharge’, which is aligned with SDG 6 of ‘clean water and sanitation’. Our strategic approach is centred around:
Minimising freshwater consumption
Exploring alternative water solutions
Increasing the use of recycled water
Replenishing groundwater
Monitoring and auditing of water consumption at end-user, withdrawal from source, water balance, quality of water, including wastewater and efficiency of wastewater treatment facility.
As part of our water stewardship journey, phase 1 of a ZLD plant, with a capacity of 4,000 KLD, was completed and made operational at Zawar Mines during FY 2023-24. It led to a reduction in freshwater dependency, thus facilitating water recovery and conservation through application of advanced technologies. It reaffirms Hindustan Zinc’s vision of zero waste and zero discharge. Work has also been initiated for a ZLD at Rampura Agucha Mine (RAM), with targeted capacity of 3,800 KLD. During the year, we commissioned a dry tailing plant and a paste-fill plant at Rajpura Dariba Complex (RDC) for saving 3,000 KLD of water with improved recovery and recycling.
These initiatives come in the wake of the expansion in capacities undertaken during FY 2022-23 at the zero liquid discharge (ZLD) plants at Dariba, Debari and Chanderiya smelting locations. Additional capacities of 3,200 KLD, 3,000 KLD and 600 KLD were made operational at these smelters, respectively.
Hindustan Zinc conducted a detailed organisation-wide water risk assessment to identify and measure the specific risks at its operating sites and its overall impact on water resources. The study involved a sensitivity analysis and stress testing for water-related risks, and calculation of a suitable water pricing structure for the Company. It was completed with the help of multiple quantitative and qualitative tools, including the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) India Water Tool, as well as the World Resources Institute (WRI) Aqueduct and Global Environmental Management Initiative (GEMI) local water tools. Using these tools, we identified and assessed the various water-related risks and developed a management strategy.
We also got a futuristic analysis done by Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas, which revealed the water-stress indicators to be high in most of our locations. We remain committed to managing the water risks through application of rigorous standards and processes, irrespective of their level.
We have continually enhanced the management of our tailings dams to create more sustainable business operations:
We have a well-articulated tailings management plan to ensure sound and safe storage. All steps are taken to effectively implement the plan, enabling a safer tailings storage facility.
Our TSF design, construction, safe operation and closure practices are benchmarked to the highest global standards, which include:
Clear policy on tailings management, with strong organisational commitment for implementation of safe and responsible practices
TSF Committee of in-house experts to strengthen compliance with the Group’s TSF standard
Selection of reputed engineering firms for TSF designing
Periodic TSF risk assessments, with mitigation plans to minimise associated risks
Tailings utilisation in back filling through paste-fill/hydro-fill
Replacement of wet tailings disposal system with dry tailings disposal
Collection and recycling of supernatant water in process
Construction of garland drains around the dams to maintain zero liquid discharge
Deployment of satellite based interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) monitoring technique to provide early warning of surface ground movements
During the year, a third-party audit was conducted to identify any deficiencies against Global Industry Standard on Tailings Management (GISTM) requirements, as per the Group’s business target to fully implement all the GISTM principles by FY 2024-25.
With its lifecycle rooted in the principles of circular economy, zinc has emerged as a major contributor to sustainable development. Its versatility and durability make it one of the most resilient and recyclable materials, and a key enabler of the mining industry’s role in promoting regenerative economy. With its growing focus on the adoption of the latest, best-in-class technologies and tools, the mining industry is surging actively towards reduction in waste generation, conservation of natural resources, promotion of energy efficiencies, and minimisation of the carbon footprint.
As a frontrunner in sustainable business development, Hindustan Zinc has prioritised circular economy and continues to invest in the latest technological advancements, to reduce waste and to promote recycling and reuse.

In a key endorsement of its successful waste reduction efforts, Hindustan Zinc received two Indian patents during FY 2023-24. The patents, titled ’Method for production of lead by performing dross removal procedures’ and ’Method for production of zinc by utilising lead plant slag’, validate our success in increasing the yield of zinc and lead through in-house innovations in pyro metallurgy.
We drive our circular economy efforts by:

In a strategic alliance aimed at advancing sustainability and maximising resource utilisation, Hindustan Zinc has partnered with Runaya Green Tech Private Limited (Runaya) to establish an Integrated Minor Metals Complex (IMMC) at Chanderiya. This collaboration underscores Hindustan Zinc’s commitment to innovative solutions and environmental stewardship.
Led by the belief that resource efficiency, environmental consciousness, and economic growth are seamlessly intertwined, Runaya stands to reshape the metals and minerals sector through its innovative approach, hinging on cutting-edge technology and a sustainable mindset, aiming to overhaul traditional practices in the industry.
Through this partnership, at the state-of-the-art IIMC facility at Chanderiya, Runaya is efficiently processing the lead and zinc residues generated by Hindustan Zinc’s smelters situated at Chanderiya, Dariba, and Debari. Embarking on a series of initiatives set to commence in FY 2024-25, the joint efforts are focussed on the recovery of various valuable metals, including cadmium, cobalt, copper, and antimony.
In FY 2023-24, this partnership, backed by Runaya’s specialised expertise, achieved remarkable milestones, significantly enhancing operational efficiency at IIMC. Through strategic debottlenecking efforts, the Company successfully increased plant capacity by 30% and improved recoveries by 5%, showcasing its focus on ‘4R’ waste strategy – ‘Reduce, Recycle, Reuse and Reclaim’, and ‘eco-friendly’ disposal of process residues. In the same period, Runaya processed a total of 20,000 MT of hazardous smelter waste, recovering 13,157 MT of metal.
With the commissioning of new plants on the horizon in FY 2024-25, a substantial increase is expected in both processing of waste and metal recovery, to 56,300 MT and 31,300 MT respectively. The Company aims to achieve 3x growth in processing and recovery, signalling its continued momentum and trajectory of growth.
Jarosite is a waste produced in the hydrometallurgy process of zinc extraction, necessitating additional investment for its stabilisation and disposal. We conducted a feasibility study, in collaboration with IIT Roorkee, to use jarosite in construction-related works, such as concrete, mortar and paver blocks, as an alternative for cement to the extent of 10%-15%.
We also partnered with some government agencies, like National Council for Cement & Building Materials (NCCBM), National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI) and Central Road Research Institute (CRRI), for the utilisation of jarosite in cement and road construction.
In FY 2023-24, Hindustan Zinc signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with VEXL Environ Projects Ltd to pioneer innovative solutions for utilisation of waste like jarofix and jarosite, generated during zinc extraction, for productive applications. The agreement was aimed at revolutionising the smelting process sustainably and forging ahead towards a greener tomorrow. Under the pathbreaking agreement, the two companies will establish a pilot plant for pioneering sustainable solutions by leveraging cutting-edge technology and expertise. The partnership sets a new benchmark for environmental responsibility and economic prosperity in the mining industry.
Jarosite used in cement construction
Jarofix used in road construction
Achieving a ‘3x increase in the gainful utilisation of smelting process waste from baseline FY 2019-20’ is one of the sustainability goals we have identified to drive sustainable future growth. In our pursuit of this goal, our Waste to Wealth Community continues to explore new ways of recycling and gainfully utilising our manufacturing waste. The community is engaged in continuous monitoring and review of the progress made by the Company towards the implementation of this sustainability goal. Based on the assessment, it develops the necessary strategies to steer the realisation of our waste related goal.
Some of the key initiatives undertaken during FY 2023-24 to make our methods and processes more efficient, sustainable, and environment-friendly included the following:
Hindustan Zinc has enhanced the intensity of its research and development (R&D) through investments in skilled scientists and technical facilities. Collaborations with world-class universities and institutes, technology providers and start-ups are an essential part of our innovation process.
The commissioning of the fumer plant at CLZS during the year was a major step towards reducing the smelter’s waste footprint. It will lead to 100% elimination of jarosite waste from one of the hydro zinc smelters and help reduce jarosite generation by 160 kt annually. The plant will further lead to reduction in the demand for land, thus saving the precious land resource.
As part of its efforts to transition to a circular economy, Hindustan Zinc conducted a workshop on ‘Extended Producers Responsibility & Waste Management‘ during the year. Important stakeholders from waste management team came together to understand the implications of EPR rules and how to efficiently handle waste.
Reduction of air emissions is a key priority at Hindustan Zinc, and we are committed to enhancing the quality of air in and around our operational areas.
The focus of these initiatives is on reducing particulate matter emissions and gases emitted by our operational activities, including mining, materials handling, processing and transportation.
We are working closely with various organisations to mitigate the negative effects of our operations on biodiversity. Our initiatives in this regard include:
We continue to make progress on our 3-year agenda to revisit our BMP for driving no net loss. The exercise, being undertaken in engagement with the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), involves:
Our strong commitment to biodiversity conservation was manifest in the Company’s participation in the task force on nature-related financial disclosures (TNFD) reporting of a risk management and disclosure framework to address the current needs of the organisation by factoring naturerelated risks and opportunities into the financial and business decisions.
We are progressing well on the study undertaken to assess the impact and dependency of our direct operations on ecosystem, and to develop BMPs for all our Rajasthanbased units. The review is being done by IUCN to identify business risks and opportunities arising from ecosystem change. During FY 2023-24, we planted 72,000 native species across Hindustan Zinc.
In December 2023, we launched Rajasthan’s first ever TACO (The Animal Care Organisation) Club at Rampura Agucha Mine, with the aim of spreading awareness and sensitivity among school children on issues related to animal cruelty and violence. The club will conduct monthly activities, exposure visits, etc.
The plan is to include 100 government schools across Rajasthan by FY 2024-25 to run the TACO club. This will be followed by further expanding the reach to 250-300 schools by next year.
We have initiated a wildlife conservation programme at Rajpura Dariba Complex (RDC) to preserve and develop the wildlife habitat in the region, along with removal of invasive species. The programme involves spreading awareness in nearby communities and schools against illegal poaching, hunting and man-animal conflict. Extension of support to the forest department for monitoring, rescue and rehabilitation of wildlife is another key initiative. The programme also covers fencing of habitat and abandoned wells to prevent decline in wildlife. It further encompasses ecological development as well as construction of water holes and water tanks. During FY 2023-24, Zawar Mines also contributed to the Rajasthan Forest Department for habitat conservation.
We have developed progressive closure plans for all our mines to ensure sustainable site closure, as and when required. We believe it is essential to have in place proper plans to identify, minimise or mitigate, and manage the various risks associated with site closure. Such risks may be environmental, socio-economic, health and safety related or reputational in nature.

We periodically communicate the progress against our closure plans to all the internal stakeholders and relevant external stakeholders in a transparent manner. We also maintain a funds corpus, held separately from our operational funds, to meet the closure costs for ensuring successful implementation of the site closure plans.